MANUFACTURING
2024/09/19
What are the characteristics of technical jobs at companies? What are Nikkiso’s strengths in particular? | Answers to questions from students
- Industrial
- Pump
- Interview
- Technology
Index
Should I work as a technical worker at a company, or stay in academia at a university or research institute to continue my research...? No doubt many students are at the crossroads of such choices.
We interviewed Shinichiro Ejiri, a pump engineer who won an award for his bold commitment to cutting-edge research, about the characteristics of research and development at companies and academia, and the differences in their areas of expertise. What can be done only by companies? What can be done only by academia? And what can be done only by Nikkiso?
| Shinichiro Ejiri: Joined Nikkiso in 2017 after working for a railway vehicle manufacturer. Mainly engaged in the research and development of centrifugal pumps in the Development Department at the Fluid Technology Center of the Industrial Division, and the Research and Technology Department at the Nikkiso Institute of Research and Technology. |
Make the impossible possible through cooperation between companies and academia

—— You won the Challenge Award of the Turbomachinery Society of Japan in September 2023. The award is given to young researchers engaged in cutting-edge research and technological development on turbomachinery. What are your thoughts on the significance of being engaged in academic research while belonging to a company?
Ejiri: The general flow of the process of socially implementing the natural sciences in the field of industrial machinery is:
(1) First, the discovery of phenomena by natural sciences (so-called fundamental research)
(2) Then, the exploration of their usefulness by engineering (so-called applied research)
(3) And finally, commercialization by industry (so-called product development)
Excluding some large manufacturer groups, a single entity alone cannot do everything in this flow from (1) fundamental research to (3) product development. So, it is important for academia such as universities and research institutes, which take charge of the upstream, and companies, which take charge of the downstream, to cooperate with each other. If each of us takes charge of roles that we are good at, we can do things that each of us cannot do alone.
In order to facilitate this cooperation, companies dealing with cutting-edge technologies need to deal with the boundary area between (2) and (3). Academic research is, therefore, one necessary function.
Research and development are worthwhile because Nikkiso deals with special liquids
—— Academia and companies are good at different areas. What are the factors behind this?
Ejiri: Since universities and research institutes do not need to seek profit, they can work on fundamental research that is difficult for companies to do. However, since they do not have personnel to operate large-scale manufacturing facilities or equipment, they do not have sufficient capacity or resources to implement their research results in society.
Compared to universities and research institutes, companies are much better at the function of manufacturing, making it easier to conduct large-scale experiments and design and manufacture experimental equipment with unique specifications.
Furthermore, companies already have a completed mechanism for manufacturing. They have people who procure components, and people in factories who actually operate manufacturing equipment. If research and development are embedded into the mechanism for manufacturing that has been built as a business, it is not very difficult to give new technologies an actual form. Taking feasibility into account, I feel that companies have more freedom in manufacturing than universities and research institutes do.

—— What kind of research and development is Nikkiso especially good at?
Ejiri: While most pumps in the world are designed to handle water, Nikkiso's pumps are basically and ultimately targeted at special liquids other than water, such as high-temperature, cryogenic, and toxic liquids. So, products are not feasible without consideration that is deeper than that for the development of normal pumps.
In the case of the research and development of mass-produced pumps, since cost benefits are important, it is necessary to focus on how to reduce costs by using generic materials. When dealing with special liquids, however, it is necessary to start consideration from the selection of materials that can withstand the properties of the liquid.
If there is an environment in which we can choose from a wider range of materials than now, we would be able to undertake development with a more challenging mindset. I think this would enable people who have studied materials to play an even more active role.
—— Is the need for special liquids growing?
Ejiri: Currently, the demand from society for hydrogen and ammonia is high in order to realize a decarbonized society. But I think there will be other needs in the future. For example, since it is predicted that space development will become more active, I personally expect potential in the liquids required for it. I believe that other companies do not have the corporate culture for dealing with challenging liquids that they have not worked on before, so Nikkiso has an advantage in the development of new pumps.
If you are serious about research and development like this, you can go one more step into a more difficult area. If you want to do something others don't do, Nikkiso is a good company to work for.
Research on rotating stall, cavitation, and other inevitable issues for pumps
—— You said that if dealing with cutting-edge technologies, it was necessary to work on not only (3) product development but also the boundary area with (2) applied research. What kind of research are you doing, Mr. Ejiri?
Ejiri: I am mainly researching rotating stalls, cavitation and industrial use of metal 3D printers. I will explain one by one.
A rotating stall is an internal flow instability that occurs when a pump is operated at a lower flow rate than the design flow rate. A rotating stall is called a rotating stall because the stalling region rotates. This phenomenon causes the pump to vibrate, leading to a deterioration of the pump and peripheral equipment.
——What is cavitation?
Ejiri: Cavitation is a phenomenon where bubbles form in the liquid in the pump. Centrifugal pumps spin a blade-equipped wheel-shaped impeller in the liquid, and use its centrifugal force to move the liquid. When the impeller is spun, the pressure on the liquid differs from place to place within the pump. Because the boiling point is lower in locations with a lower pressure, the liquid may vaporize and bubbles may form. This mechanism is the same as that by which the air becomes thinner (atmospheric pressure drops) and water boils below 100°C as you clime a mountain.
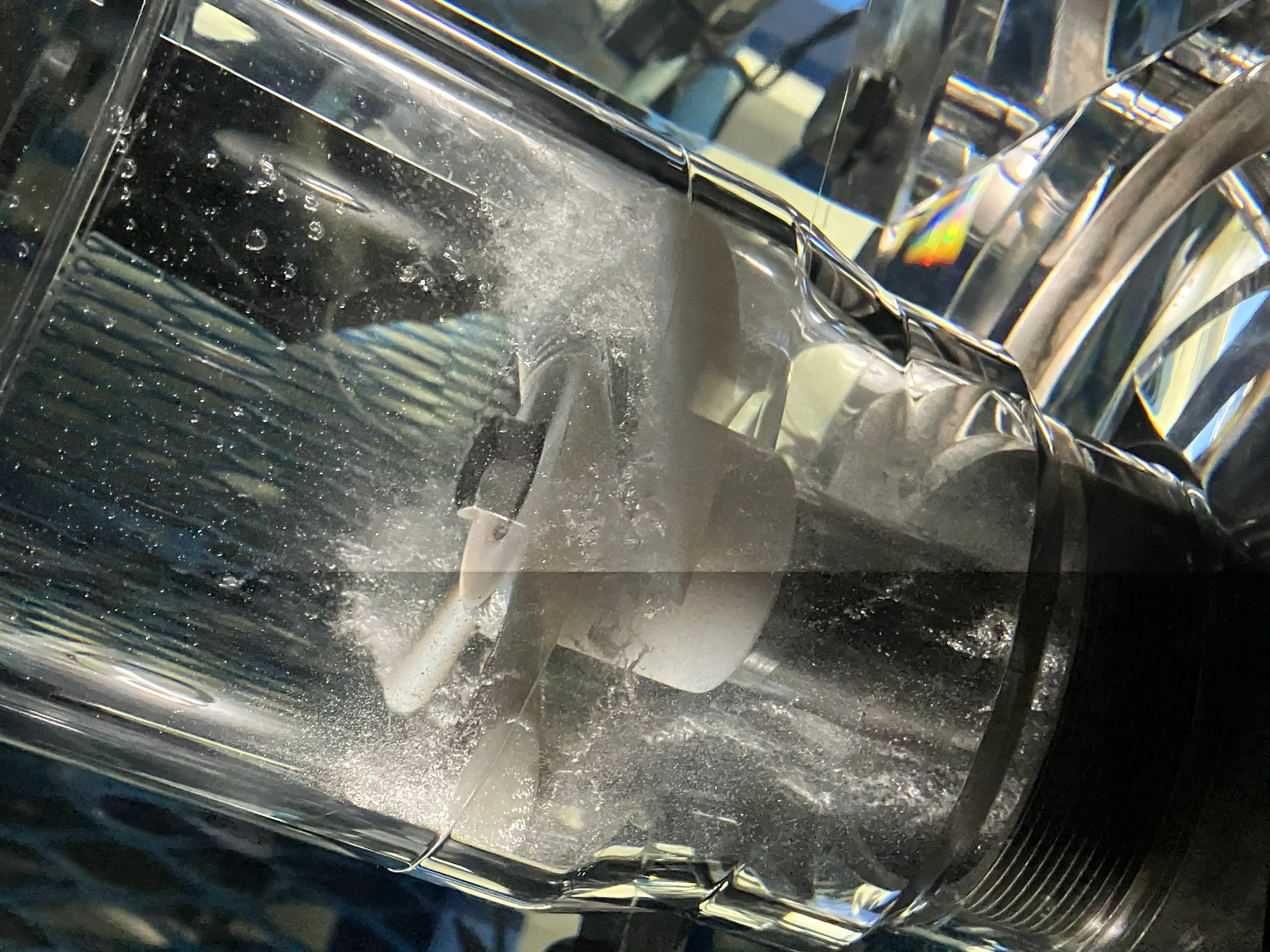 Bubbles near an impeller caused by cavitation inside a pump
Bubbles near an impeller caused by cavitation inside a pump
Because a pump is designed to be filled with liquid, it cannot achieve its intended performance if bubbles form in the liquid.
The research on rotating stall and cavitation is being carried out in collaboration with a lab at Osaka Institute of Technology in Osaka.
—— Can rotating stall and cavitation occur in many kinds of pumps?
Ejiri: Yes. As such, they are inevitable issues for pumps. Although they have been researched for a long time, the detailed mechanisms of their occurrence and how to prevent such phenomena have not yet been fully explained. It is a challenging issue, but we are continuing our research to make pumps work more safely.
——What is the research on metal 3D printers?
Ejiri: Our research is on using metal 3D printers to manufacture pump impellers. Centrifugal pumps with special specifications for delivering liquid such as liquefied natural gas are manufactured in small quantities, and pumps with similar specifications might be manufactured only once every few years or decades.
So, if a manufacturing process using casting is applied, there are some issues, including the risk that formwork stored for a long period of time may deteriorate over time. To solve this problem, we are considering manufacturing impellers using metal 3D printers.
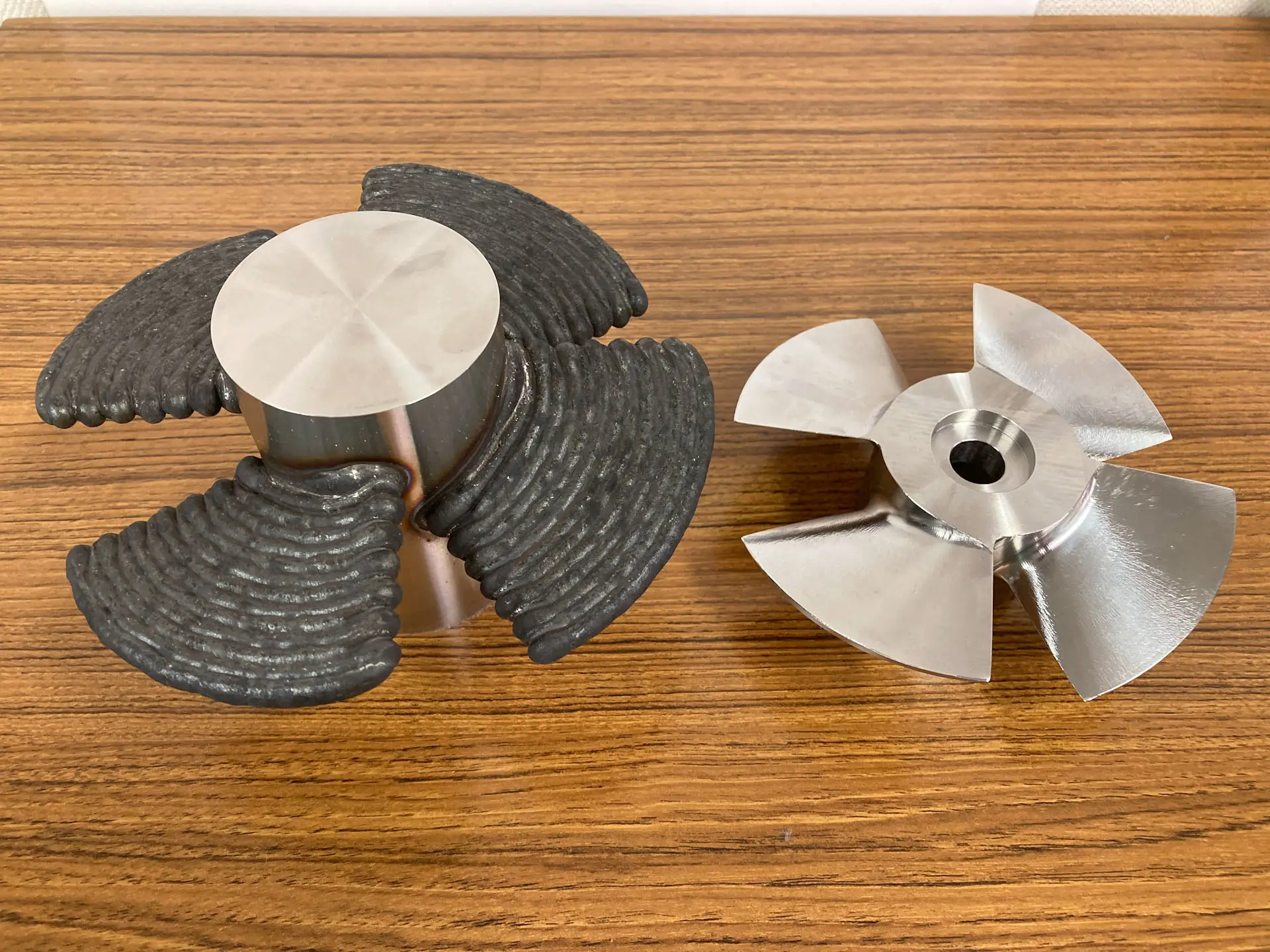

Manufacturing process of an impeller using a metal 3D printer. After lamination on the left side, and after finishing on the right side
Science and technology have no national boundaries. Findings are shared as common property
——You actively disseminate the results of such research and development outside the company through academic conference presentations and other opportunities. What is your intention?
Ejiri: Science and technology have no national boundaries, and the attitude of trying to solve everything within a single company does not produce quick and valuable output. I believe, therefore, that building relationships outside the company is also an important point. Of the research results produced by Nikkiso, I think we can disclose information that Nikkiso does not need to monopolize.
The basic approach of academic societies is to improve society as a whole by each member bringing knowledge in their areas of expertise, so I present my research results as much as I can.
——What are your aims and feelings about students in the joint research with the lab at Osaka Institute of Technology?
Ejiri: We are trying to provide as much experience as possible that is difficult to get only at a university.
For example:
- We invite students to factories of Nikkiso and its partner companies, and encourage them to observe the actual manufacturing processes of various components and products
- With the cooperation of the engineers at the factories we teach the work on site and to work together with them
- Students present their research results to engineers in the company and discuss it with them
and so on.
I would like to encourage students who receive a hybrid education from both a university and a company to join a manufacturer, even if it is not Nikkiso, in order to revitalize the industry as a whole. But if you want a job where you have a lot of discretion, please join Nikkiso!
Pickup
-
 MEDICAL FIELD
MEDICAL FIELD
Empowering Asia’s Expanding Dialysis Treatment with Nikkiso’s Advanced Technology and Comprehensive Support
- Hemodialysis
- Interview
- Medicalbusiness
2025/10/30
-
 MANUFACTURING
MANUFACTURING
Pumps also actively used in semiconductor manufacturing: 20 years of history of compact, high-speed canned motor pumps
- Technology
- Interview
- Pump
- Semiconductor
2025/05/21
-
 MANUFACTURING
MANUFACTURING
Nikkiso's DX initiatives: CAE Support Department continues to evolve, aiming to eliminate dependence on the skills and expertise of specific people
- Technology
- Interview
2025/04/09
関連記事
-
 MANUFACTURING
MANUFACTURING
Pumps also actively used in semiconductor manufacturing: 20 years of history of compact, high-speed canned motor pumps
- Technology
- Interview
- Pump
- Semiconductor
2025/05/21
-
 MANUFACTURING
MANUFACTURING
Nikkiso's DX initiatives: CAE Support Department continues to evolve, aiming to eliminate dependence on the skills and expertise of specific people
- Technology
- Interview
2025/04/09
-
 MANUFACTURING
MANUFACTURING
Behind the development of the 3D Sinter, a new technology which serves to improve both the quality of SiC power semiconductors and productivity in the manufacturing process
- Semiconductor
- Interview
- Technology
- Industrial
2025/02/19
-
 MANUFACTURING
MANUFACTURING
Efficiently Manufacturing Eco-Friendly Aircraft Components with CFRTPs | Initiatives for Decarbonization in the Aviation Field
- Interview
- Aircraft
- Aerospace
- Technology
2024/05/16




