MANUFACTURING
2023/09/26
What is an MLCC? Here’s some information spanning from basic knowledge to the “Warm Isostatic Laminator”, a device serving to support the manufacturing of MLCCs
- Technology
- Interview
- Industrial
Index
In the mid-1980s, as the miniaturization of home appliances was seeing progress, mobile phones were developed, and the demand for inexpensive, compact, and high-quality MLCCs grew. Against this backdrop, Nikkiso developed the “Warm Isostatic Laminator” in response to requests received from electronic component manufacturers. The Warm Isostatic Laminator is a pressing device which achieves high-precision and high-quality pressure processing.
The Warm Isostatic Laminator has established itself as a world-standard machine, with more than 600 units currently in operation around the world.
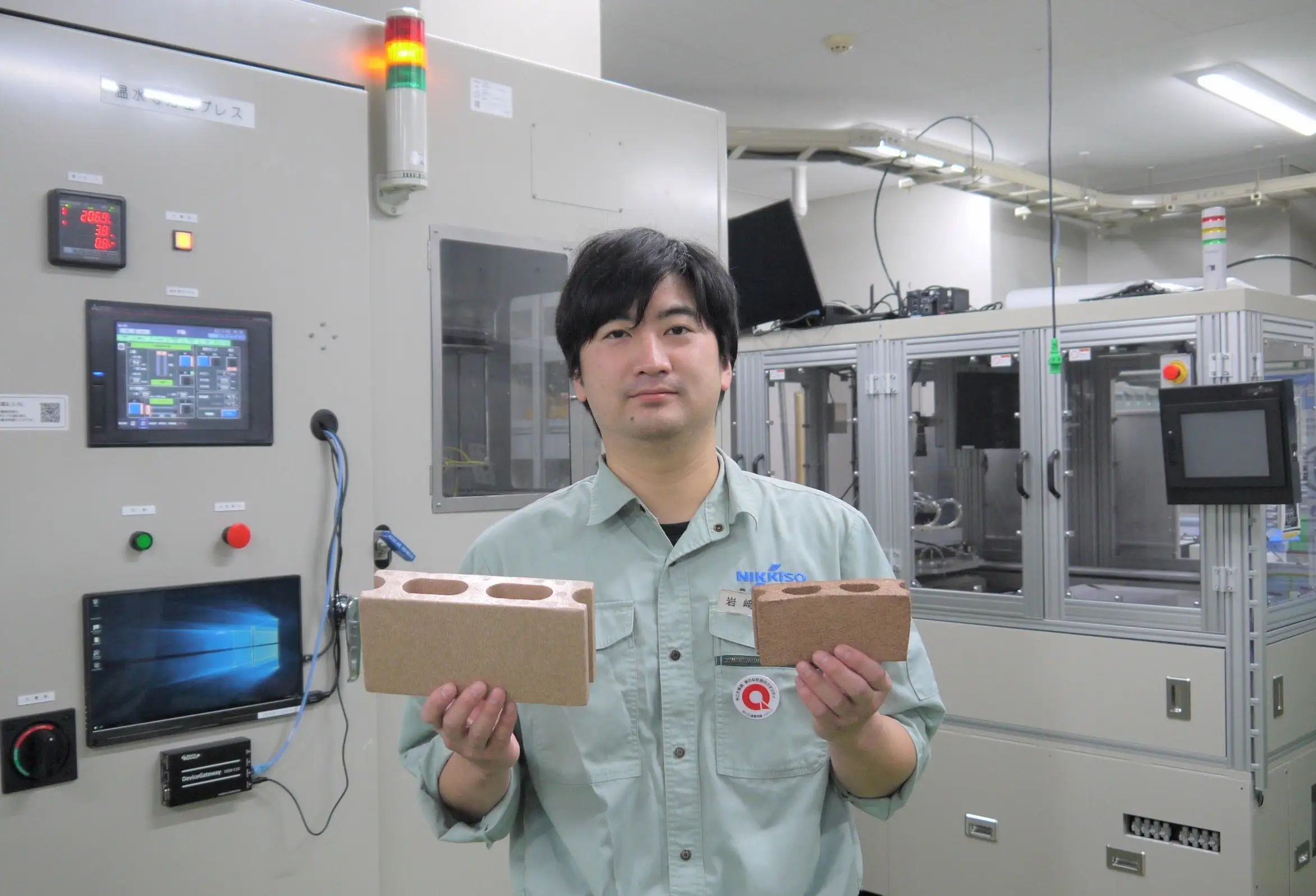
This time around, we interviewed Tatsuya Iwasaki, who is involved in development for the Warm Isostatic Laminator and other equipment used for the manufacturing of electronic components. We talked in detail about everything spanning from basic knowledge related to MLCCs, the characteristics of the Warm Isostatic Laminator produced by Nikkiso, the R&D journey, to future prospects.
| Tatsuya Iwasaki joined Nikkiso in 2013. He joined the Development Group at the Precision Engineering Center of the Industrial Division and worked on the development of equipment used for the manufacturing of electronic components. |
The MLCC is a component commonly used in electronic equipment
――This time around, the themes of conversation are going to be the electronic component MLCC and the Warm Isostatic Laminator, which serves to support the manufacture of MLCCs. First, could we please have an overview of the MLCC?
Iwasaki: The MLCC, or Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitor, is a type of electronic component. It is made by superimposing thousands of layers of ceramic sheets with electrodes printed on them and which are only a few hundred microns thick. These are then subjecting the crimping and tempering to produce the MLCC.
――In what situations are MLCCs used and how do they work?
Iwasaki: MLCCs are used in a variety of electronic devices, such as smartphones, televisions, and personal computers. They play an important role in maintaining a constant voltage and in removing noise from current.
Demand for these components is on the rise, as they are used in the fields of IoT and AI, which are fields that have recently been attracting attention. Such demand is also on the rise when it comes to electric vehicles (EVs), which are expected to become widespread in the future.
The global market is expected to grow at a compound annual rate of 11.93% between 2021 and 2027, reaching US $34.1651 billion by 2027.
[See: Global Information; “[English Market Research Report] Global Multilayer Ceramic Chip Capacitors (MLCC) Market”]
How MLCCs are manufactured
――Can you please provide details on how MLCCs are manufactured?
Iwasaki: First, we print electrodes and wiring on what’s called a green sheet, which is comprised of a thin, evenly spread, paste-form ceramic that has been dried. Sheets which have been subject to printing are then stacked one on top of the other. Next, the stacked sheets are pressed and tempered at a high temperature of several thousand degrees. Then, they are finally cut out to the size corresponding to the type of parts they are going to be used for.
――What are the key points involved in the MLCC manufacturing process?
Iwasaki: When applying pressure to the laminated sheets, it is important to apply pressure at a temperature which has the binder (binding agent) contained within the ceramic sheet softening well. The Warm Isostatic Laminator manufactured by Nikkiso is characterized by excellent performance in that respect.
Nikkiso’s Warm Isostatic Laminator, which uses the power of water to apply pressure
――What kind of device is the Warm Isostatic Laminator? Can you please provide an overview and give details on the features of the Warm Isostatic Laminator provided by Nikkiso?
Iwasaki: The Warm Isostatic Laminator is a device that applies pressure using the power of water. Water is heated to a temperature that is matched with the type of binder so that pressure can be applied from all directions while maintaining that temperature.
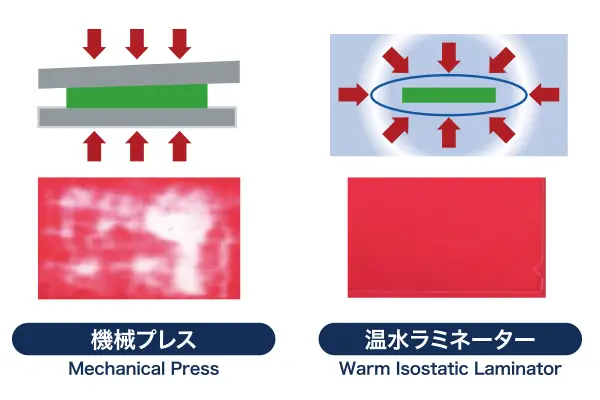
Products that Nikkiso works on deploy a unique “pin closure system,” which seals pressure vessels using latches called pins. This system allows for the circulation of water within the pressure vessel, thereby achieving uniform temperature in the vessel.
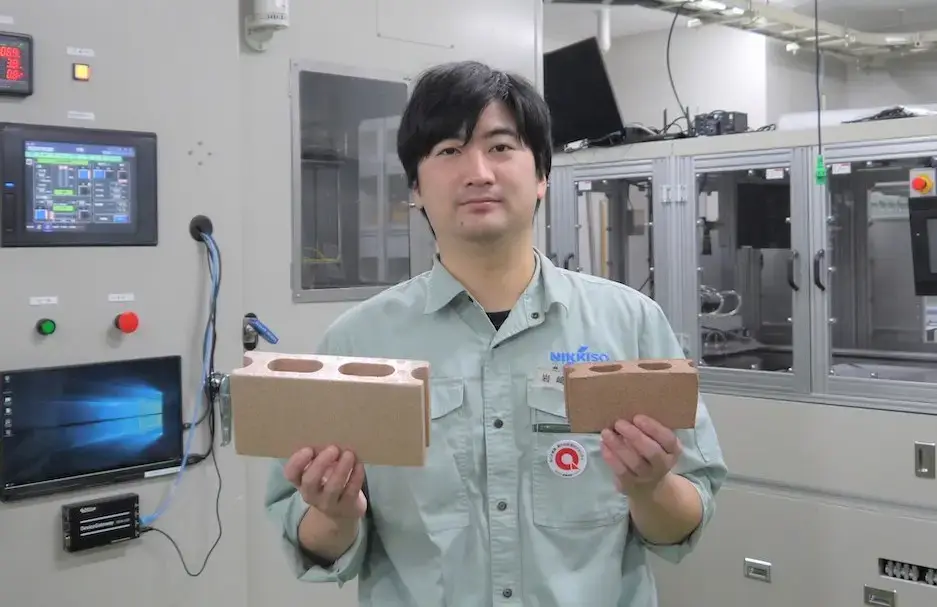 With the Warm Isostatic Laminator, a block of Styrofoam (shown on the left) can be compressed to one size smaller (shown on the right) while having its shape retained.
With the Warm Isostatic Laminator, a block of Styrofoam (shown on the left) can be compressed to one size smaller (shown on the right) while having its shape retained.
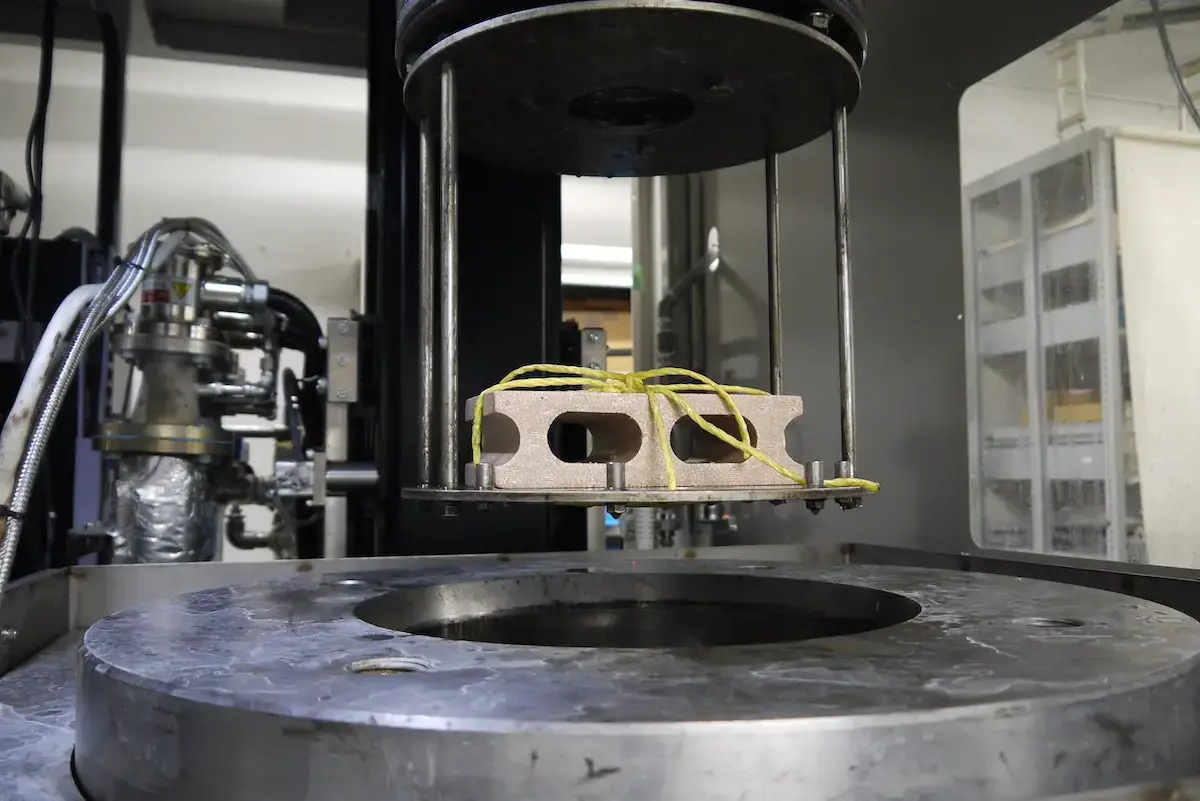 Setting of a block of Styrofoam within a Warm Isostatic Laminator
Setting of a block of Styrofoam within a Warm Isostatic Laminator
――Please tell us about how Nikkiso came to work on the development of the Warm Isostatic Laminator and what things were like when development was taking place.
Iwasaki: Originally, Nikkiso had been providing a cold isostatic press to customers, which works by applying pressure using cold water instead of warm water. Amid that situation, the demand for MLCCs grew, and we began to develop a hydraulic press, or warm isostatic laminator, which would be able to apply heat. This is something we went about doing at the request of electronic component manufacturers.
At the beginning of development, there seemed to be many difficulties involved, such as not being able to have the pressure increase all that well, and not being able to maintain pressure levels. After a process of trial and error and continuous improvements, the product was finally complete.
As a result, we have sold a total of 600 Warm Isostatic Laminators, mainly to major Japanese electronic component manufacturers. We currently have a domestic market share of more than 90%.
Continuing to lead the industry with high value-added Warm Isostatic Laminators that focus on production efficiency.
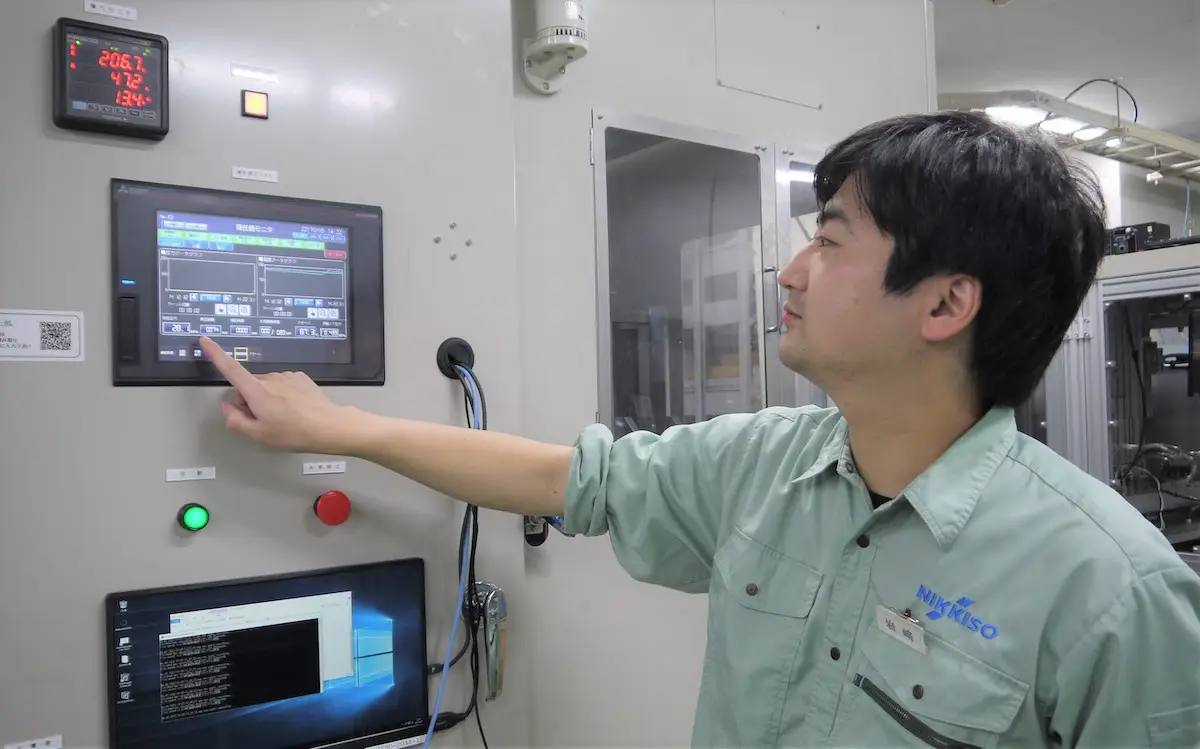

――Can you tell us about the kind of evolution achieved when it comes to Nikkiso’s Warm Isostatic Laminator?
Iwasaki: In 2016, we undertook a revamping of our devices against the backdrop of the market entry of overseas manufacturers and the intensifying price competition we were seeing. A new version of the Warm Isostatic Laminator was released. It was characterized by space-saving features which allowed for productivity to be increased by placing more devices in the same area, energy-saving features which enabled the maintenance of elements such as heaters without draining the water out of the device, and labor-saving features which served to enhance operability and maintainability with a touch panel.
In 2021, we released what we called the “Warm Isostatic Laminator with Preheat-Loader” which has been designed specifically to improve production efficiency. Our main target for the product was the Chinese market. By automating the process of placing products in the pressure vessel, this device facilitates the achievement of higher productivity levels than that offered by other manufacturers.
――What kind of development projects are you currently working on?
Iwasaki: We are currently developing a system that leverages AI to predict failures.
For example, if a notification can be provided beforehand to the effect that a failure is likely to occur, or to the effect that parts need to be replaced after a few more instances of use, one can prepare for such failures by performing maintenance or purchasing replacement parts in advance.
As a result of that, we hope to minimize the down time of equipment and contribute to increasing efficiency when it comes to production undertaken by customers.
――Please tell us about the frame of mind behind your involvement in the R&D and manufacturing of MLCCs.
Iwasaki: We are involved in the whole process spanning from development to delivery. And thanks to the immense levels of positive feedback we’ve received, we maintain a realization throughout our involvement to the effect that we have been able to contribute to the enhancement of production when it comes to MLCCs.
Also, the feeling I get, is that having lots of discussions with electronic component manufacturers who are attracting attention worldwide constitutes a very good learning experience as an engineer.
――Thank you. Last question: What is your outlook on the future?
Iwasaki: In order to continue being the industry leader when it comes to Warm Isostatic Laminators, we want to go about improving upon our equipment by undertaking the continuous refinement of that product.
It is my hope that we will continue to contribute to the evolution of the electronic component industry by incorporating real feedback from more and more electronic component manufacturers in the process, and approaching development in a manner which has us being there for customers every step of the way as we work to produce what they need.
Pickup
-
 MEDICAL FIELD
MEDICAL FIELD
Empowering Asia’s Expanding Dialysis Treatment with Nikkiso’s Advanced Technology and Comprehensive Support
- Hemodialysis
- Interview
- Medicalbusiness
2025/10/30
-
 MANUFACTURING
MANUFACTURING
Pumps also actively used in semiconductor manufacturing: 20 years of history of compact, high-speed canned motor pumps
- Technology
- Interview
- Pump
- Semiconductor
2025/05/21
-
 MANUFACTURING
MANUFACTURING
Nikkiso's DX initiatives: CAE Support Department continues to evolve, aiming to eliminate dependence on the skills and expertise of specific people
- Technology
- Interview
2025/04/09
関連記事
-
 MANUFACTURING
MANUFACTURING
Pumps also actively used in semiconductor manufacturing: 20 years of history of compact, high-speed canned motor pumps
- Technology
- Interview
- Pump
- Semiconductor
2025/05/21
-
 MANUFACTURING
MANUFACTURING
Nikkiso's DX initiatives: CAE Support Department continues to evolve, aiming to eliminate dependence on the skills and expertise of specific people
- Technology
- Interview
2025/04/09
-
 MANUFACTURING
MANUFACTURING
Behind the development of the 3D Sinter, a new technology which serves to improve both the quality of SiC power semiconductors and productivity in the manufacturing process
- Semiconductor
- Interview
- Technology
- Industrial
2025/02/19
-
 MANUFACTURING
MANUFACTURING
What are the characteristics of technical jobs at companies? What are Nikkiso’s strengths in particular? | Answers to questions from students
- Industrial
- Pump
- Interview
- Technology
2024/09/19




