ENRICH OUR LIVES
2023/04/18
Decarbonizing the Shipping Industry:The Role of LNG-powered Ships
- Decarbonation
- LNG
- Ship
- Pump

Index
Adopted in 2015 against the backdrop of worsening climate change, the Paris Agreement raised net-zero emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases (GHGs) as one of the long-term global goals. And today, countries around the globe are advancing efforts to achieve this goal.
With this groundswell in the background, reducing GHG emissions has also become an urgent challenge in the field of international shipping. In this article, we will describe the LNG-powered ships that are attracting attention as a means of decarbonizing the shipping industry.
Background to decarbonizing the shipping industry
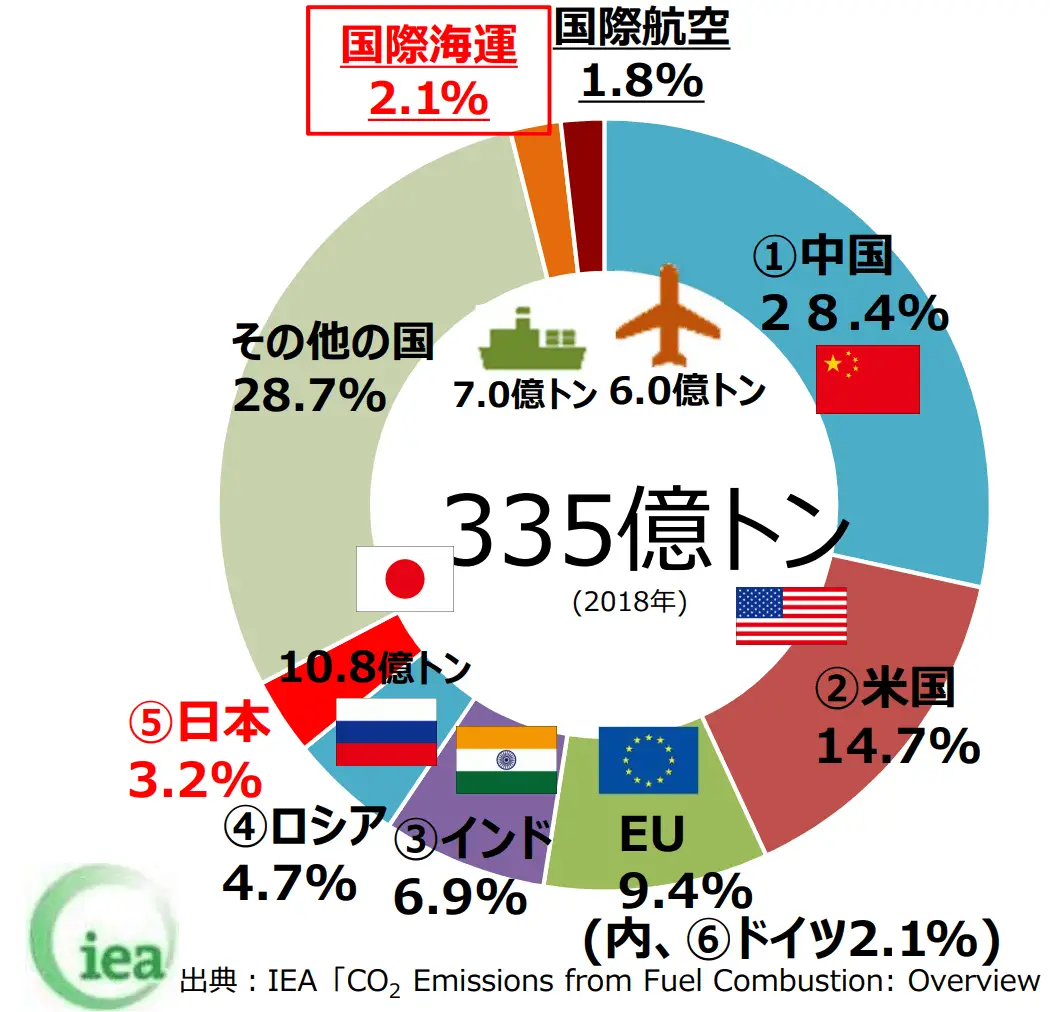
(Source: Maritime Bureau, "Initiatives to Achieve a Low-carbon and Decarbonized Maritime Sector")
Carbon dioxide emissions from the international shipping sector account for approximately 2.1% of all global GHG emissions. Due to the increase in maritime cargo volumes, however, carbon dioxide emissions are projected to increase to approximately 7.0% (approx. 2.11 billion tons) of the total by 2050 if no action is taken.
Global demand for ocean transport rose steadily from 1985 to 2019, and although it did decline 4% year-on-year in 2020 due to the impact of COVID-19, it is expected to continue increasing as the global economy recovers and grows.
(Reference: Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism “Initiatives to Achieve a Low-carbon and Decarbonized Maritime Sector” and The Japanese Shipowners' Association “SHIPPING NOW 2021-2022 Data Edition”)
In light of these projections, reducing carbon dioxide and other GHG emissions has become an urgent issue for the international shipping sector.
What are greenhouse gases (GHGs)? GHGs include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and other gases that cause a greenhouse effect. And it is believed that global warming will intensify as surface and air temperatures rise due to increasing concentrations of GHGs in the atmosphere. In an effort to reduce GHG output, the Japanese government announced that it will curtail GHG emissions 46% by 2030 (compared to fiscal 2013 levels), and that it will continue to undertake the challenge of achieving a 50% reduction. |
Efforts to decarbonize the shipping industry
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) adopted a strategy to reduce GHG emissions in April 2018 in an effort to decarbonize the international shipping sector. This strategy raised the following three numerical targets using 2008 as the base year.
- Improve the average efficiency of overall international shipping 40% by 2030
- Reduce total GHG emissions from international shipping 50% by 2050
- Achieve zero GHG emissions from international shipping as early as possible during this century
At present, the IMO is studying measures to achieve these targets, while Japan, one of the world's largest shipping nations, established the International Shipping GHG Zero Emissions Project as a collaborative effort between industry, academia, and the public sector, through which it has been actively making studies and proposals.
Among the various measure candidates intended to achieve these targets, the adoption of alternative ship fuels is drawing attention from a long-term perspective. Although today’s shipping industry mainly uses heavy fuel oil for ships, LNG, ammonia, hydrogen, and carbon recycled methane are being considered for use as alternatives to this fuel.
In particular, the number of LNG-powered ships has been increasing recently.
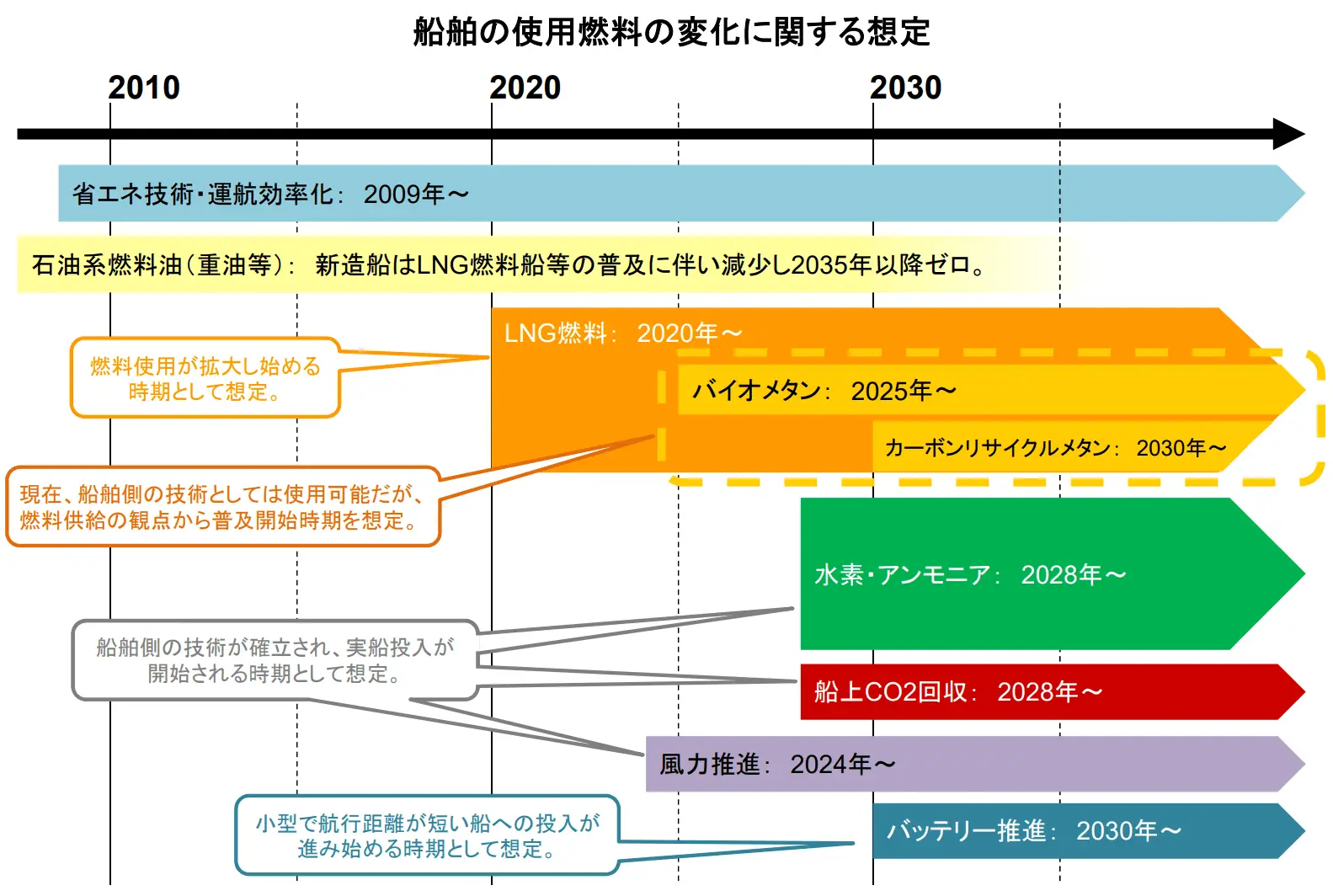
(Source: Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism “Roadmap for Zero Emissions from International Shipping”)
What are LNG-powered ships?
LNG-powered ships are ships that run on LNG as fuel. The number of LNG-powered ships has been increasing rapidly, from just 32 in service in 2012 to 191 in 2020.
(Reference: DNV “LNG External Webinar -11 May 2021”)
| What is LNG? LNG (liquefied natural gas) is essentially natural gas, which primarily consists of methane, that has been liquefied by cooling to -162°C . Clear, colorless, and odorless, this liquid has a volume of 1/600th that of its gaseous state, which allows it to be transported in large quantities by sea. In addition to ship fuel, it is widely used throughout the world for city gas, and as a fuel for thermal power generation, automobiles, and industrial applications. |
Reasons for the rapid increase in LNG-powered ships
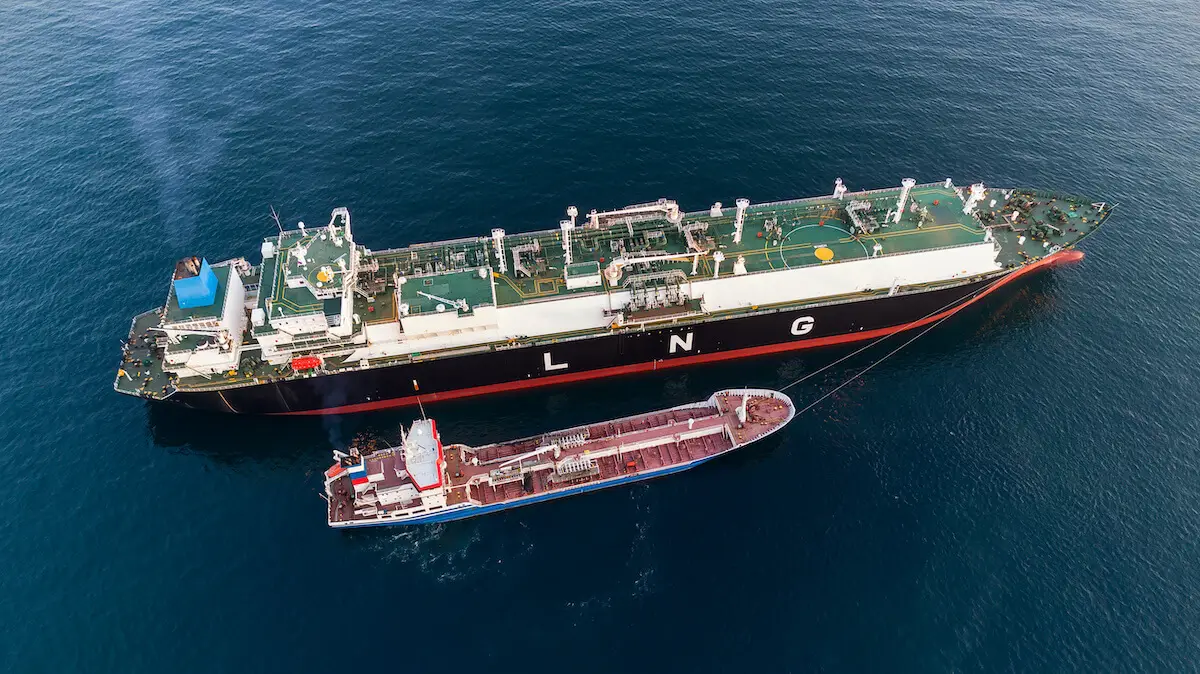

Among the various alternative fuels, why are ships that use LNG attracting so much attention? The following highlights and details the three main reasons.
1.LNG is an energy source with a low environmental impact
The first reason is the low environmental impact of LNG when used via combustion. LNG is capable of curtailing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions as compared with other fossil fuels, which means it helps reduce GHG emissions.
In addition, combusting LNG does not generate any sulfur oxides (SOx), dust, or other similar biproducts that can cause acid rain and air pollution. Compared to heavy fuel oil, some data even show that LNG can reduce emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) by approximately 30% depending on the type of engine. In the future, replacing standard LNG with carbon recycled methane, which is produced using a technology called methanation that synthesizes methane from CO2 and hydrogen, is expected to transform LNG into an emissions-free fuel.
2.LNG has strong price competitiveness compared with other alternative fuels
Another reason is that LNG has stronger price competitiveness than hydrogen, biofuels, and other alternative fuels. Although capital investments are required for specially designed engines and cryogenic tanks that are compatible with LNG fuel, the relatively low running costs are also a driving factor behind its adoption.
3.LNG has already been commercialized and infrastructure is being built
Most importantly, LNG is the only alternative fuel candidate that has already been commercialized as a ship fuel. As with LNG, hydrogen and ammonia fuels are also being considered for decarbonizing the shipping industry. However, these present a variety of remaining issues, including:
- Consideration of specifications and usage methods based on the toxicity of ammonia, the low density of hydrogen, and other characteristics
- Development of engines capable of directly combusting hydrogen and ammonia
- Securing of a stable supply
Therefore, although studies are underway, commercialization has not yet been achieved.
On the other hand, there are already many LNG-powered ships in service, mainly in Northern Europe. Even Japan launched its first LNG-powered ship in 2015. The market for engines and other types of LNG-fuel-compatible equipment has also been established, and the environment for its further diffusion is starting to be put in order, with international standardization for operations and fuel supply methods, as well as consideration of safety requirements, underway.
Nikkiso's high-pressure fuel supply system supports LNG-powered ships
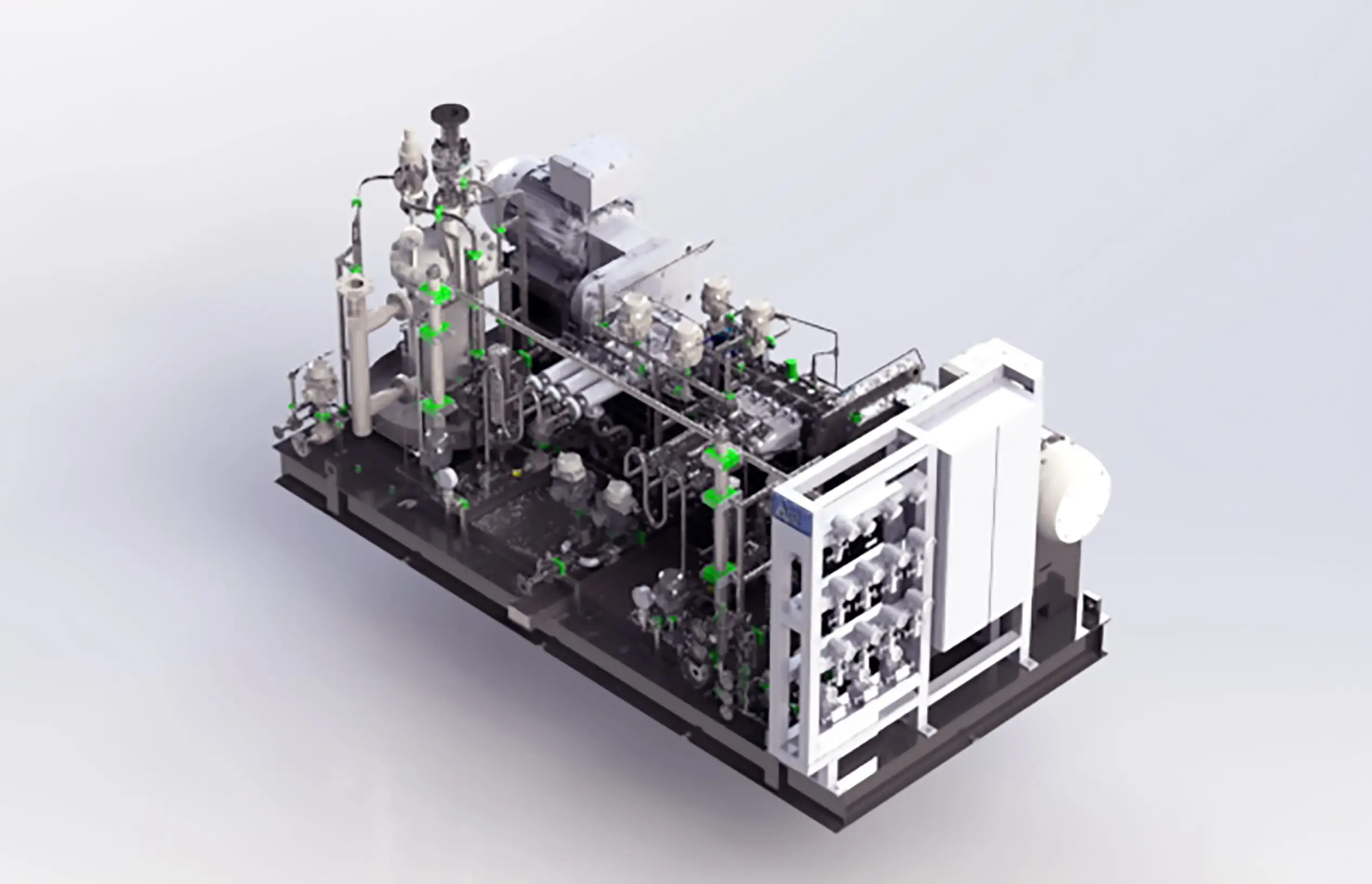
The Nikkiso Group designs, manufactures, and sells high-pressure fuel supply systems that feed high-pressure fuel to LNG-powered ship engines.
Because high-pressure engines require natural gas to remain at a pressure of about 30 MPa, this system packages pumps for boosting pressure, high-pressure vaporizers for vaporizing LNG, various valves, and instrumentation in a compact manner. In order to ensure a stable supply of fuel in the unlikely event of a failure, each system is equipped with two pumps (one of which is a backup), yet is still compact.
Although LNG-powered ships are still relatively new, The Nikkiso Group has accumulated significant experience and know-how ever since we delivered these systems for the world's first LNG-powered ships, thereby earning the trust of many customers. And orders have increased rapidly as the market has grown, with the number received in fiscal 2021 reaching approximately 10 times that of the previous year.
Future outlook for the Nikkiso Group
The Nikkiso Group offers various pumps for extremely low-temperature use, high-pressure fuel supply systems for LNG-powered ships, BOG re-liquefaction systems for recovering boil-off gas (BOG), heat exchangers, and other types of equipment.
In order to address the recent growth in demand for LNG-powered ships and high-pressure fuel supply systems in Asian’s shipbuilding industry, we have determined to build new LNG-related equipment manufacturing and testing facilities in Busan, South Korea, and Hangzhou, China. We will further strengthen our manufacturing organization and service capabilities in support of diffusing LNG-powered ships.
Summary
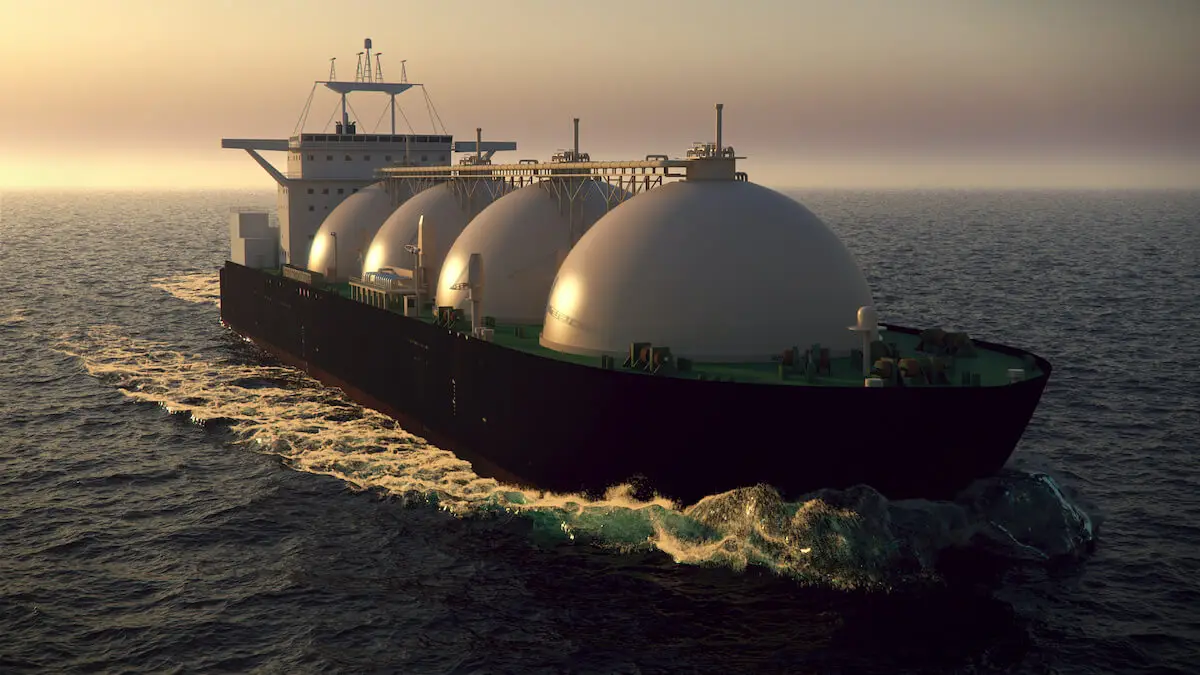

LNG has attracted attention as a promising alternative fuel for decarbonization because of its low environmental impact and strong price competitiveness. And against the backdrop of stricter environmental regulations in the shipping industry, the number of LNG-powered ships in actual service has been increasing rapidly.
The Nikkiso Group possesses the technological capabilities to achieve high quality in the design and manufacture of high-pressure fuel supply systems for LNG-powered ships, which is why we are chosen by many customers.
Please contact Nikkiso for any questions or concerns regarding LNG-powered ships, as well as new pumps and systems for alternative fuels.
Pickup
-
 MEDICAL FIELD
MEDICAL FIELD
Empowering Asia’s Expanding Dialysis Treatment with Nikkiso’s Advanced Technology and Comprehensive Support
- Hemodialysis
- Interview
- Medicalbusiness
2025/10/30
-
 MANUFACTURING
MANUFACTURING
Pumps also actively used in semiconductor manufacturing: 20 years of history of compact, high-speed canned motor pumps
- Technology
- Interview
- Pump
- Semiconductor
2025/05/21
-
 MANUFACTURING
MANUFACTURING
Nikkiso's DX initiatives: CAE Support Department continues to evolve, aiming to eliminate dependence on the skills and expertise of specific people
- Technology
- Interview
2025/04/09
関連記事
-
 ENRICH OUR LIVES
ENRICH OUR LIVES
How does an airplane stop? Secrets of the cascade, an essential component for deceleration
- CFRP
- Aircraft
- Aerospace
2024/09/12
-
 ENRICH OUR LIVES
ENRICH OUR LIVES
Secret to the Odor of Gas
- Pump
- LNG
- Industrial
2024/05/08
-
 ENRICH OUR LIVES
ENRICH OUR LIVES
What exactly is the SiC power semiconductor that is essential for decarbonization and the popularization of EVs? Here is some basic knowledge and information on future prospects
- Decarbonation
- Technology
- Industrial
- Semiconductor
2023/11/20
-
 ENRICH OUR LIVES
ENRICH OUR LIVES
Decarbonizing the skies with hydrogen aircraft? Useful basic knowledge, the state of development, and everything in between
- Hydrogen
- Decarbonation
- Aircraft
- Pump
- CFRP
- Industrial
2023/10/17





